Book now online or call (03) 9783 9041.
Muscle pain can be often referred to as “muscle strain”. This is when there is tearing to the fibres in the muscles due to excess pressure or strain onto the area. Tearing to the muscle can lead to bleeding and irritation to local nerve endings.

Signs and symptoms:
- Pain at rest
- Bruising
- Weakness in the muscles
- Swelling, bruising, redness to the area
- Immobility
Causes:
- Repetitive activities
- Poor posture
- Direct trauma
Treatment:
Osteopathic treatment may include soft tissue massage, joint mobilisation and articulation. We also provide advice regarding lifestyle management. Osteopaths also provide rehabilitative exercises to build strength in the affected region. Depending on the cause of the injury whether it be acute or chronic we will form a treatment plan to decrease the likelihood of recurrence.
Reference:
Muscle strain. WebMD. Retrieved from http://www.webmd.com/fitnessexercise/guide/musclestrain
Tennis elbow (lateral epicondylitis) & Golfers elbow (medial epicondylitis)
What is it?
Wrist extensors are a group of muscles that are located along the outer forearm and are responsible for wrist and finger extension. These muscles come together to form a tendon which attaches on to the outer aspect of the elbow. Commonly, repetitive wrist extension and excessive load placed on this area can cause damage to the tendon leading to pain and inflammation along the outer aspect of the elbow, often referred to as Tennis elbow. Forearm flexors are a group of muscles that are located along the inner aspect of the forearm. These muscles come together to form a tendon and attach along the inner aspect of the elbow. Damage to this area results in pain and inflammation which is commonly known to as Golfer’s elbow.
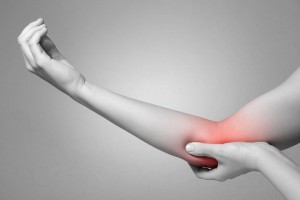
Signs and symptoms:
- Pain on wrist extension/wrist flexion
- Neck and upper back stiffness
- Pain along the forearm muscles which may be a constant ache, or give sharp pain with activities
or extensor compartment
- Constant ache, sharp pain with activities
- Decreased strength in grip
- Elbow stiffness worse in the morning
Causes:
Common causes include repeated wrist extension often involved in sporting activities such as tennis. Other causes include occupational activities such as labour intensive work (i.e. computer use and carpentry).
Treatment:
During the acute stage, ice and analgesics are recommended coupled with stretching and manual therapy. A combination of soft tissue therapy, joint mobilisation, trigger point release and stretching may be effective to treat tennis elbow. Muscle strengthening exercises may also be beneficial. Other treatment modalities include taping and bracing.
Reference
Brukner, P., & Khan, K. (2008). Clinical Sports Medicine (3rd ed.). Mc Graw Hill Australia Pty Ltd.
Plantar fasciitis
What is it?
Plantar fascia is connective tissue that runs from the base of the heel to the sole of the foot. Plantar fasciitis is when there is pain and damage to the affected area due to overstretching or increased tension on the structure. Following damage there is inflammation. It is one of the most common cause of heel pain in clinical practice.
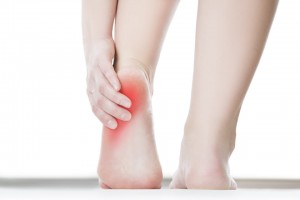
Signs and symptoms:
- Sharp pain along the base of the foot
- Heel pain that is worse after periods of inactivity
- Swelling in the heel
- Calf tightness
- Flat feet or high arches (risk factors)
Causes:
Causes of plantar fasciitis may be due to overuse associated with wear and tear or due to trauma increase force through the area more than what it can withstand. Risk factors include
poor foot posture, foot or ankle stiffness, poor footwear and muscle weakness
Treatment:
A combination of soft tissue therapy, joint mobilisation, trigger point release and stretching may be effective to treat plantar fasciitis. Osteopaths will also examine the knee, hip and lower back to treat secondary compensations. Treatment will also involve exercises and stretches to strengthen the plantar fascia, decrease inflammation and pain in affected areas.
Reference
Foot problems: heel pain. (2015). Retrieved from
http://www.betterhealth.vic.gov.au/bhcv2/bhcarticles.nsf/pages/foot_problems_heel_pain

